Bariatric Surgery
July 30, 2014
 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 35.7% of adults and 17% of children and adolescents are obese in the United States. This growing epidemic is not only costly to our country, but also has overwhelming effects on an individual's overall health. Additionally, obesity is a risk factor associated with metabolic syndrome, which can raise one's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other health problems. An option that some obese people have is bariatric surgery. This option can significantly reduce an individual's body mass index (BMI) and aid them in leading a healthier life. Here to answer a few, common questions about this topic is Scott Welle, DO, FACOS, FACS. Dr. Welle is a board certified osteopathic general surgeon with advanced specialty training in minimally invasive, robotic, and bariatric surgery. Dr. Welle's office is Tucson Bariatric, located at 4715 E. Camp Lowell, 520-319-6000. Or for more information about Dr. Welle and/or bariatric surgery go to http://scottwelledo.com/.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 35.7% of adults and 17% of children and adolescents are obese in the United States. This growing epidemic is not only costly to our country, but also has overwhelming effects on an individual's overall health. Additionally, obesity is a risk factor associated with metabolic syndrome, which can raise one's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other health problems. An option that some obese people have is bariatric surgery. This option can significantly reduce an individual's body mass index (BMI) and aid them in leading a healthier life. Here to answer a few, common questions about this topic is Scott Welle, DO, FACOS, FACS. Dr. Welle is a board certified osteopathic general surgeon with advanced specialty training in minimally invasive, robotic, and bariatric surgery. Dr. Welle's office is Tucson Bariatric, located at 4715 E. Camp Lowell, 520-319-6000. Or for more information about Dr. Welle and/or bariatric surgery go to http://scottwelledo.com/.
Q-Can you explain to our readers what bariatric surgery is and what it aims to achieve in terms of patient outcomes?
Bariatric surgery is commonly called weight-loss surgery. It is performed on people who are morbidly obese and suffer from a number of obesity related diseases, like high blood pressure or diabetes. Weight loss is achieved by reducing the size of the stomach and sometimes rerouting the small intestine, making it so people are full more quickly and often feel less hungry. Depending on which surgery you have, expected weight loss is between 50 and 90% of your excess weight. It is successful in achieving substantial, long-term weight loss in nine out of 10 people who undergo the surgeries.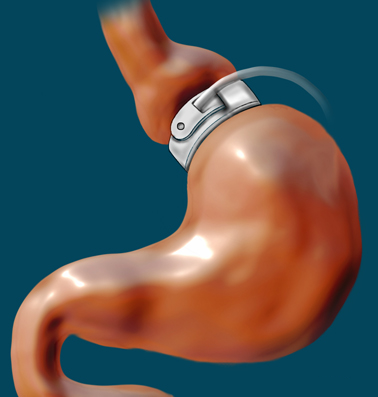
Q-Are there different types of bariatric surgery?
There are several different types of bariatric surgery. The most commonly performed surgeries, and the ones that I perform, are the adjustable gastric band (pictured on the right), vertical sleeve gastrectomy, and Roux-n-Y gastric bypass. Other surgeries performed are the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch and the gastric plication.
Q-What are some common characteristics of individuals that would be recommended for bariatric surgery?
Most patients are at least 80 pounds overweight, and many suffer from obesity related medical problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or sleep apnea.
Q-After an individual receives bariatric surgery, will they need to undergo any additional surgeries?
Most patients will not need to undergo additional surgeries specifically related to their bariatric surgery. However, some patients develop gallbladder problems requiring their gallbladder to be removed. Some patients elect to undergo plastic surgery to remove excess skin. Long-term complications requiring additional surgeries are not common.
Q-Is plastic surgery necessary after substantial weight loss?
Plastic surgery is not necessary after substantial weight loss. However, some patients choose to have excess skin removed from places like their abdomen, thighs or arms. Some women choose to have a breast lift or augmentation as well.
Q-What is the average weight loss for a patient who undergoes bariatric surgery?
Weight loss following bariatric surgery varies depending on which procedure you have done. Expected weight loss following an adjustable gastric banding is about 40 to 50% excess bodyweight. Whereas following a gastric bypass, expected weight loss is about 80% excess body weight loss. Your excess weight is determined by subtracting your ideal body weight based on height from your current body weight.
Q-How long does it take to complete one of these surgeries?
That depends on the surgery. A robotic gastric bypass takes about 60 to 90 minutes. A sleeve takes just under an hour and a band is usually only 30 to 45 minutes.
Q-How long is the recovery time?
Most patients spend one night in the hospital. They are usually back to their regular activities and back to work in about a week. However, they are on lifting restrictions for about a month, so they do not develop hernias at the incision sites.
Q-What kind of post-surgery guidelines do you recommend to your patients to help them lead a healthier life?
After surgery we encourage a high protein, low carbohydrate diet. We also encourage an active lifestyle with regular exercise. To help our patients  with these lifestyle changes, we have a dietitian and psychologist in our office for support before and after surgery. We also have agreements with several gyms around town for discounted memberships. Additionally, we have monthly support groups at the hospital. Attendance is strongly encouraged.
with these lifestyle changes, we have a dietitian and psychologist in our office for support before and after surgery. We also have agreements with several gyms around town for discounted memberships. Additionally, we have monthly support groups at the hospital. Attendance is strongly encouraged.
Q-Is bariatric surgery an option for those suffering from metabolic syndrome? If so, at what point should weight loss surgery be considered?
Bariatric surgery is an option for people suffering from metabolic syndrome. The surgeries have been shown to improve if not "cure" diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. The sooner the better. The surgeries become less effective the longer a patient has been treated for these problems. So surgery should be considered early on in the disease course.
Q-Is bariatric surgery an option for people with diabetes? If so, at what point should those with diabetes consider weight loss surgery?
Yes, bariatric surgery is an option for people with diabetes. Many studies have shown that bariatric surgery is a better treatment for diabetes. In many cases after surgery, we are able to get people completely off of their diabetes medicines and achieve excellent control of their sugars. The sooner the better. The surgery is less effective at resolving the diabetes the longer a person has been treated for diabetes.
Q-The Journal of the American Medical Association recently published a study that found obesity surgery may keep diabetes in remission, even after 15 years in some individuals. What could complicate this? Why doesn't every patient have this long-lasting effect?
This study didn't stratify the duration of diabetes treatment for the patients. It simply looked at patients that had diabetes or not. Diabetes is a progressive disease. The longer a person has diabetes the more common it is that they will have to increase either the dosage of their oral medications, the number of their oral medications or sometimes even progress to requiring insulin to manage their diabetes. The further along a patient is in their progression of their disease, the less effective the surgeries become. For example, a patient that has been on multiple oral medications or insulin we may be able to decrease their medications but not get them completely medication free. Whereas a newly diagnosed diabetic on one diabetic medication, we often are able to get them medication free and have their diabetes go into complete remission.
Q-What are the common causes that lead bariatric surgery to fail?
 The most common cause for long-term failures is a lack of maintaining their lifestyle changes and patients will resume their old habits. This usually occurs when patients fail to follow up with their surgeon. During the follow-up visits we check to make sure that patients are continuing their lifestyle changes. And we stress routine follow-up with our dietitian, psychologist and attend our support groups to help patients continue their lifelong lifestyle change.
The most common cause for long-term failures is a lack of maintaining their lifestyle changes and patients will resume their old habits. This usually occurs when patients fail to follow up with their surgeon. During the follow-up visits we check to make sure that patients are continuing their lifestyle changes. And we stress routine follow-up with our dietitian, psychologist and attend our support groups to help patients continue their lifelong lifestyle change.
Is there anything else you would like to add?
Bariatric surgery is not a magic bullet and it is not an "easy way out" to lose weight. To be successful requires lifelong commitment and lifestyle changes. These surgeries are merely tools that are more effective than any other treatments that we can offer.

